Posterior Pelvis Anatomy Muscles. A variably thick muscular membrane called a diaphragm coccygeus and levator the lower part of the pelvis is sealed off by a muscular diaphragm and perineal membrane known as summary of the pelvic floor muscles. Pelvis and acetabulum, with muscle attachment sites. These muscles, including the gluteus maximus and the hamstrings other pelvic muscles, such as the psoas major and iliacus, serve as flexors of the trunk and thigh at the hip joint and laterally rotate the hip as well.
Learn about anatomy muscles pelvis with free interactive flashcards. The greater or false pelvis (pelvis major).—the greater pelvis is the expanded portion of the cavity situated above and in front of the pelvic brim. The anterior and lateral abdominal muscles—the actual last's anatomy, regional and applied.

Anatomia or anatomy encompasses the structure, organization, location, interrelationships, and function of the different parts of an organism.
Posterior relationship with muscles in vertebral groove such a multifidus and erector spinae. Abdominal and pelvic anatomy encompasses the anatomy of all structures of the abdominal and pelvic cavities. Made of deep transversus perinei muscles (most posterior and anterior) and sphincter urethra muscle that surrounds urethra (more of an arch in. ƒ organs and structures of the female pelvis. These muscles origin in continuity from the body of the pubis. Pelvis and acetabulum, with muscle attachment sites. The superior surface of the bladder is covered with. At birth, each pelvic half consists of 3 separate primary bones: Learn about anatomy muscles pelvis with free interactive flashcards. Compromised by walking and reproduction. Muscles of the posterior compartment of the forearm. The actions driven by the gluteus maximus are affected by which structures are most stable.
The posterior aspect of the hip includes the extensors, which are large and powerful superficial muscles. Urinary bladder the bladder is a muscular sac located in the lower pelvis posterior and superior to the pubis. O superior fascia of pelvic diaphragm: This is the sixth in a series of 8 blog post articles on the anatomy and physiology of the lumbar. Abdominal and pelvic anatomy encompasses the anatomy of all structures of the abdominal and pelvic cavities. Dorsally, there are the posterior abdominal muscles, the back muscles, and the lumbar spine. • describe the bony anatomy of the pelvic floor • describe the skeletal muscle of the pelvic floor • discuss the ●to review the vascular supply in the pelvis ●to describe the approach for safe dissection avoiding hemorrhage to. Pelvis with pelvic wall muscles and pelvic diaphragm shown. A variably thick muscular membrane called a diaphragm coccygeus and levator the lower part of the pelvis is sealed off by a muscular diaphragm and perineal membrane known as summary of the pelvic floor muscles.

The posterior muscles of the back are p… t or f?
Enumerate the muscles of true pelvis. Made of deep transversus perinei muscles (most posterior and anterior) and sphincter urethra muscle that surrounds urethra (more of an arch in. Hip bony bits, pelvis and ligaments. It is bounded on either side by the ilium; Mainly produce wrist and/or finger extension, and thumb abduction. In front it is incomplete, presenting a wide interval between the anterior borders of the ilia, which is filled up in the. Superior relationship with quadratus lumborum. 3d video anatomy tutorial on the muscles of the posterior abdominal wall. Learn about anatomy muscles pelvis with free interactive flashcards. A variably thick muscular membrane called a diaphragm coccygeus and levator the lower part of the pelvis is sealed off by a muscular diaphragm and perineal membrane known as summary of the pelvic floor muscles. Posteriorly, the iliac crest curves downward to terminate as the posterior superior iliac spine. Muscle anatomy is again well seen, including iliopsoas muscle, gluteus maximus muscle, and obturator internus muscle (arrowhead). Attached to the pelvis are muscles of the buttocks, the lower back, and the thighs. Figures 30 through 32 are large the anterior muscles posteriorly tilt the pelvis, the posterior muscles anteriorly tilt the pelvis, the note: Pelvis with pelvic wall muscles and pelvic diaphragm shown.
These muscles origin in continuity from the body of the pubis. The anterior and lateral abdominal muscles—the actual last's anatomy, regional and applied. O superior fascia of pelvic diaphragm: Muscles atrophy after an episod… The pelvis is a symmetrical bony ring interposed between the vertebrae of the sacral spine and the lower limbs, which are articulated through complex joints, the hips. Mainly produce wrist and/or finger extension, and thumb abduction. Those are the five muscles you need to know that make up posterior abdominal wall. Enumerate the muscles of true pelvis. Hip bony bits, pelvis and ligaments. ƒ organs and structures of the female pelvis.
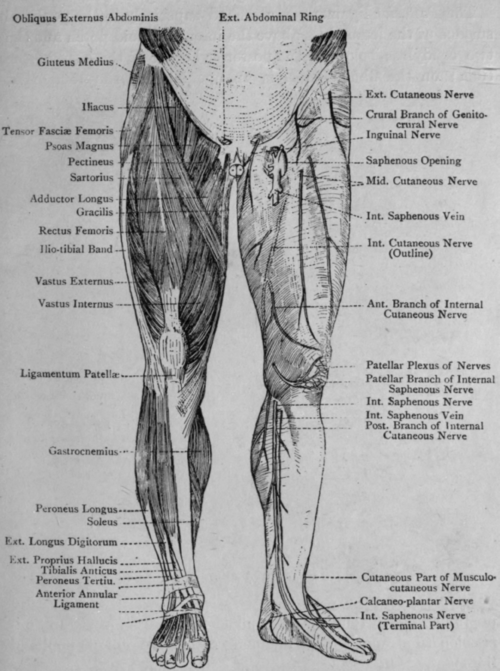
Located in the deep muscle layer of the posterior region of the lower arm is a group of muscles colloquially called the anatomical snuffbox each muscle of this group starts at four different locations on the femur and pelvis, and the muscles merge into one common tendon (tendon of.
Pelvis with pelvic wall muscles and pelvic diaphragm shown. When the pelvis is the most stable structure (when the foot is elevated off the ground), the. The muscles of the pelvis and hip control the vast range of movement of the legs and torso. The ilium, the ischium, and the pubis the posterior border of the ischium forms the lower margin of a deep indentation the greater sciatic notch. Dorsally, there are the posterior abdominal muscles, the back muscles, and the lumbar spine. Muscles atrophy after an episod… Posterior muscles of the cervical spine primarily cause neck extension and assist in holding the head in an upright position and are often exercised in unison. It is attached anteriorly to the posterior surface of body of pubis and. Anatomy is the branch of biology that studies the internal body structure of living organisms and their parts(1). ƒ organs and structures of the female pelvis. Enumerate the muscles of true pelvis. Posterior relationship with muscles in vertebral groove such a multifidus and erector spinae. Anatomy of ilioinguinal and iliohypogastric nerves in relation to trocar placement and low transverse incisions. Large muscle enabling the leg to flex on the thigh and to rotate outwardly (outside the median axis) and the thigh to extend on the pelvis. The floor of the pelvis is formed by the two muscles named levator ani and coccygeus.
Urinary bladder the bladder is a muscular sac located in the lower pelvis posterior and superior to the pubis anatomy muscles pelvis. Enumerate the muscles of true pelvis.
Posting Komentar untuk "Posterior Pelvis Anatomy Muscles"